From: Search Engine Land
Yesterday, Google webmaster tools launched Index Status (available under Health) that charts the number of indexed pages for your site over the last year.
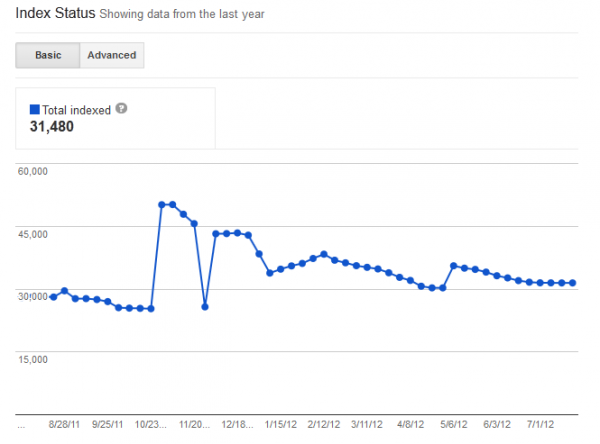
Total Indexed Count
Google says that this count is accurate (unlike the site: search operator) and is post-canonicalization. In other words, if your site includes a lot of duplicate URLs (due to things like tracking parameters) and the pages include the canonical attribute or Google has otherwise identified and clustered those duplicate URLs, this count only includes that canonical version and not the duplicates. You can also get this data by submitting XML Sitemaps but you’ll only see complete indexing numbers if your Sitemaps are comprehensive.
Google also charts this data over time for the past year.
Advanced Status: How This Data Is Useful and Actionable
The Advanced option provides additional details:
Great, right? More data is always good! Well, maybe. The key is what you take away from the data and how you can use it. To make sense of this data, the best approach is to exclude the Ever Crawled number and look at it separately (more on that in a moment). So, you’re left with:
- total indexed
- not selected
- blocked by robots
The sum of these three numbers tells you the number of URLs Google is currently considering. In the example above, Google is looking at 252,252 URLs. 22,482 of those are blocked by robots.txt, which is fairly straightforward. This mostly matches the number of URLs reported as blocked under Blocked URLs (22,346). Unfortunately, it’s become difficult to look at the list of what those URLs are. The blocked URLs report is no longer available in the UI, although it is available through the API. That leaves 229,770 URLs. Which means 74% of the URLs weren’t selected for the index. Why not? Is this bad? The trouble with looking at these numbers without context is that it’s difficult to tell.
Let’s say we’re looking at a site with 50,000 indexable pages. Has Google crawled only 31,480 unique pages and indexed all of them? (In this case, all of the not selected would be non-canonical URL variations with tracking codes and the like.) Or has Google crawled all 50,000 (plus non-canonical variations) but has decided only 31,480 of the 50,000 were valuable enough to index? Or maybe only 10,000 of those URLs indexed are unique, and due to problems with canonicalization, a lot of duplicates are indexed as well.
This problem is difficult to solve without a lot of other data points to provide context. Google told me that:
“A URL can be not selected for indexing for many reasons including:
- It redirects to another page
- It has a rel=”canonical” to another page
- Our algorithms have detected that its contents are substantially similar to another URL and picked the other URL to represent the content.”
If the not selected count is solely showing the number of non-canonical URLs, then we can generally extrapolate that for our example, Google has seen 31,480 unique pages from our 50,000-page site and has crawled a lot of non-canonical versions of those pages as well. If the not selected count also includes pages that Google has decided aren’t valuable enough to index (because they are blank, boilerplate only, or spammy), then things are less clear.
If 74% of Google’s crawl is of non-canonical URLs that aren’t indexed and redirects, is that a bad thing? Not necessarily. But it’s worth taking a look your URL structure. Non-canonical URLs are unavoidable: tracking parameters, sort orders, and the like. But can you make the crawl more efficient so that Google can get to all 50,000 of those unique URLs? Google’s Maile Ohye has some good tips for ecommerce sites on her blog. Make sure you’re making full use ofGoogle’s parameter handling features to indicate which parameters shouldn’t be crawled at all. For very large sites, crawl efficiency can make a substantial difference in long tail traffic. More pages crawled = more pages indexed = more search traffic.
Ever Crawled
What about the ever crawled number? This data points should be looked at separately from the rest as it’s an aggregate number from all time. In our example, 1.5 million URLs have been crawled. But Google is currently considering only 252,252 URLs. What’s up with the other 1.2 million? This number includes things like 404s, but tor this same site, Google is reporting only 5,000 of those, so that doesn’t account for everything. Since this count is “ever” rather than “current”, things like 404s have surely piled up over time. This count also includes URLs that no longer exist and maybe even things like CSS and JS files. I have a question into Google about that.
In any case, I think this number is much more difficult to gain actionable insight from. If the ever crawled number is substantially smaller than the size of your site, then this number is very useful indeed as some problem definitely exists that you should dive into. But for the sites I’ve looked at so far, the ever crawled number is substantially higher than the site size.
Site size can be difficult to pin down, but for those of you who have good sense of that, are you finding that most of your pages are indexed?